I would like to thank CCYAN for providing me this opportunity to patriciate in Digestive Disease Week (DDW) 2021. One of the sessions that I attended is “Empowered Crohn’sDisease Care: Targets, Tools and Talking Patients”. From this session, I have learned about the use of treat-to-target approach to treat Crohn’s Disease (CD), the tools that may help risk stratify patients with CD, and about the personalized approach to CD care. The session was split into three presentations, which were presented by Dr. Parambir S Durai, Dr. David T. Rubin and Dr. Corey A. Siegel respectively.
1) Treating to Target: Aiming for Endoscopic and Symptomatic Remission
By Dr. Parambir S Durai
What is the study about?
Dr. Durai presented about the use and benefits of a treat-to-target strategy in CD aimed at deep remission.
Presentation summary:
We need to understand how this treat-to-target approach work. Treat-to-target approach which is also known as a tight control strategy is used to achieve sustained disease control. Target and risk will be set during this time, assessment and continued monitoring have to be done to ensure targeted outcome has been reached. The most important goal in this treat-to-target approach is to achieve endoscopic healing, normalized quality of life and absence of disability.
The different studies mentioned in the presentation aimed to give CD patients early therapy using a treat-to-target approach. Treat-to-Target approach will be able to prevent adverse long-term outcomes. The studies suggest that the non-conventional methodsused at early treatment stage or frequently brings out positive outcomes to patients’remission.
Treat-to-target is treating CD patients until they achieve the desired target for the CD patients like us is healing. Healing can be mucosal healing where we go for endoscopy and the colon looks normal with no inflammation or ulceration. In some cases, there might even be histology healing which means when biopsy has done towards the colon or small bowel there is no inflammatory cells seen. In the case of a patient has fistula, then the target is to have closure of fistula. To achieve this target, the patient needs to be put under full remission.
According to Dr. Durai, patients whose response to the treatment by improvement in biomarkers results shown reduction in CRP and calprotectin. They may go for symptomatic remission. The next target is to achieve deep remission by continuing assessment and monitoring. At this stage, if the response is good, patient will be able to experience the huge improvement in symptoms, better quality of life, decreased in hospitalization and finally free from surgeries and disability and any serious disease- related complications.
Although the opportunities are huge and will provide patients with better quality of life or even achieving the absence of disability, there are some challenges that still exist in this approach. The first challenge is that treat-to-target is a time and commitment needed to follow through this approach as it needs more follow ups and more complexity of individualized process with the already busy clinical team. The other barrier is lack of knowledge of what might happen to patients later. Both patients and clinical team need to understand the limitation and provide active disease control to the patients.
2) Clinical Decision Tools: Assessing Risk and Taking Action
By Dr. Corey A. Siegel
What is the study about?
In his presentation, Dr. Siegel briefed about the importance of clinical decision support tools and suggested using clinical decision support tools to risk stratify patients for individualized CD care.
Presentation summary:
What are clinical decision tools? Dr. Corey explains that the decision-making tools are guidelines for medical providers to follow through different process based on different parameters. The tools can help to enhance medical decisions with provided clinical knowledge, patients information and other related information. And from the data gathered, doctors can formulating a diagnosis, assessing patients level of risk and help practitioner to improve the way they make decision to select medication for their patients from result shown from the tools.
Practitioner can apply several types of clinical decision support tools which has been developed such as AGA Clinical Decision Tool, IBD CDST, or CDPATH.
What can we learn from this presentation?
This tools help practitioner to decide right medication for patients based on the balance of risks and benefits especially at the early stage or before they develop complications.
By using these tools, it may help to reduce practitioners from making any risk of misdiagnoses and medication errors.
The tools improve efficiency and patients’ satisfaction.
. Give more confidence to practitioners to recommending right therapy and apply more aggressive monitoring technics.
3) Shared Decision Making in CD: The Path to Improving Quality of Life
By Dr. David T. Rubin
What is the study about?
Dr. Rubin discussed about the complexity of shared decision making for patient-centered and empowered CD care.
Presentation summary:
Dr. Rubin informed that the shared decision making involves three different parties. They are: -
1. Patient
- Person who suffer with IBD and request treatments.
2. Doctors/ IBD Nurses
- Medical provider who have fundamental knowledge about the disease and therapies which can be used to treat IBD.
3. Payor
- Person/company/agency who pays for the care and treatments for the patient.
To make the relationship between the three parties happen there are several factors that should take to consideration by all the parties. Refer to diagram below:-
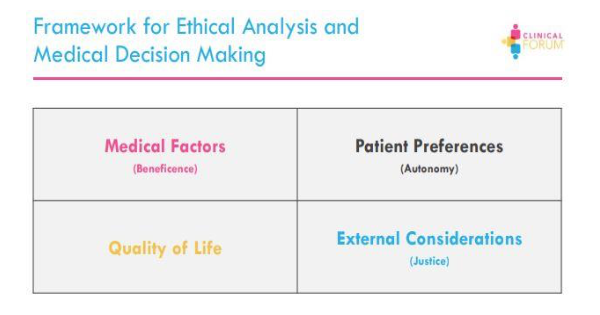
He further explains that, for each patient, the provider and payor must consider four variables: efficacy, safety, convenience and access. These variables help to makeprogress and provide better care for the patients. Practitioners can use “Ethical Analysisand Medical Decision Making” framework to make difficult medical decision. This can help to strengthen the doctor-patient relationship.
a. Medical Factor (Beneficence)
- This is a value in which the provider takes actions or recommends courses thatare in the patient’s best interest. The principle is based upon the objective assessment of a doctor, and what they feel is best for their patient. The points of concerns are:-
What is the patient’s medical problem? diagnosis? prognosis?
What are the treatment goals?
What are the therapies recommended?
What are the risk factors of the recommended therapies as well as the disease itself?
How are patients benefited by medical and nursing care?
How can harm be avoided?
b. Patient Preferences (Autonomy)
- Refer to the patient’s right to make decisions for themselves according to theirown preferences. They can either agree to take treatment or refuse the treatment. The points of concerns are:-
Patient’s right to accept a treatment.
Reasons for patient’s refusal of treatment.
c. Quality of Life
- A major goal of medical treatment is to restore, maintain, or improve quality of life. Care management in treat-to-target should address the patients’ life goalsand include long term plan for stability and health. Quality of life is important in CD patients and their symptoms are directly proportional to the quality of thepatient’s life. The points of concerns are:-
Perception of quality of life
Normalization of symptoms
d. External Considerations (Justice)
- Involves provider bias or influences, resource allocations and payor decisions which effects the delivery of care for patients. Payors normally balance a budget and distribute their resources which might not be enough for the care the providers think optimum for the patient. There are differences in the providers view of what is needed and the payors view of what could be distributed in term of resources. Payor can look at different solutions to be more cost-effective, be more engaging in disease managements and partner up with experts to identify better support care for patients. The points of concerns are:-
What are the financial and economic factors involved in CD care?
Are there any problems for resource allocation?
Do payors have enough budget to cover the treatment?
Dr. Rubin gave us an overview of how decision in CD are made and the complexity of it involving the three parties. Although decisions are individually based on differing onpriorities and values, the ultimate goal should be the patients’ sustained functionalremission. Therefore, the three parties involved should figure out how to care for CD patients and optimize the quality of life and involve payor more in the CD care.
In summary, treat-to-target could be an effective way of treating CD patients with applying proper decision-making tools and involving all the decision makers (patient, provider and payor) to provide a better care, early treatment and allocate resources optimally.